This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Breast biopsy
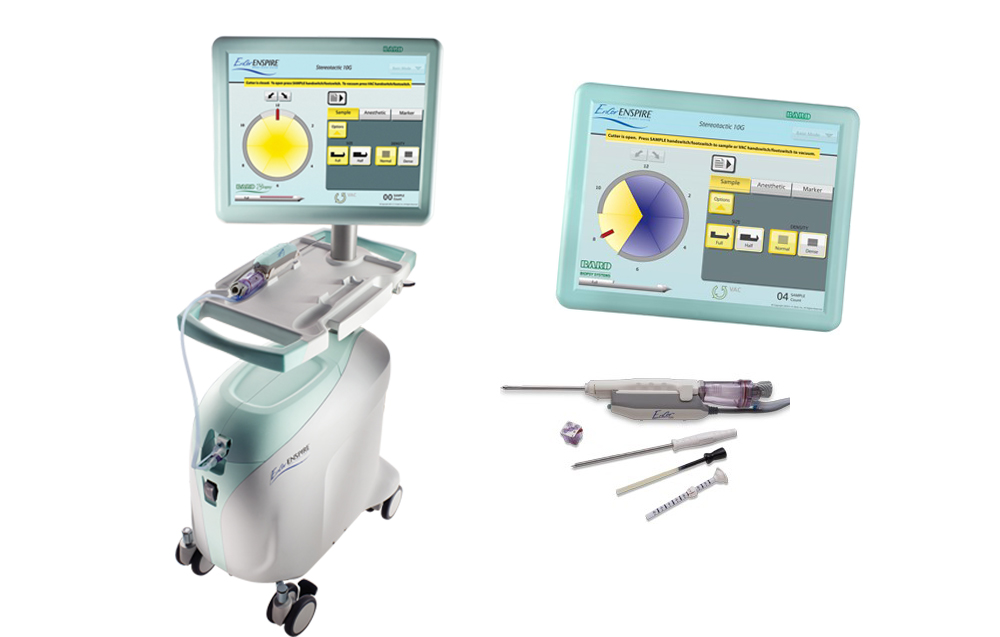
VAB - Vacuum Assisted Biopsy
Currently, VAB is the most modern and precise method of examining breast changes, used as a standard in the best centers in the world.
Vacuum assisted biopsy is a comfortable and painless procedure consisting of excision of the entire breast tumor or taking samples from a suspected tumor for diagnosis. The collected material is immediately sent for histopathological examination. It is always performed when a change in the mammary gland is visible during ultrasound or mammography.
At the Medycyna Dąb clinics in the city of Warsaw, Katowice, vacuum assisted biopsy has been performed for many years, we also successfully use it to remove lesions up to 2 cm, with a safety margin. This treatment is performed privately using the latest technologies and state-of-the-art apparatus. VAB is performed under local anesthesia. During the entire procedure, the specialist observes the correctness and progress of breast lump removal on the ultrasound screen.
Advantages of vacuum assisted biopsy
First of all, attention should be paid to the fact that a vacuum assisted biopsy is a minimally invasive procedure, as there is no incision or unsightly scar, no sutures or deformation of the breast. It is also a suitable form of examination for patients who have undergone surgery on breast lumps and with polycystic degeneration. An additional advantage is the fact that the vacuum assisted biopsy takes only 10-15 minutes. The health benefits of its implementation are much higher than the financial costs incurred.
Vacuum assisted biopsy is often the only method of diagnosis or treatment of women with breast implants as the risk of damaging the prosthesis is negligible.
It can be concluded that a vacuum assisted biopsy has only advantages, but it has one limitation – the size of a solid nodule, i.e. about 2 cm. Waiting too long can cause the tumor to grow, and then the only way to get rid of the lump is to have a cut and stay in the hospital
Painless

No surgery

No sutures

No scar

No stay at the hospital

l Quick 10-15 minutes

Frequently asked questions
Patients often ask if the need for a vacuum assisted biopsy means that they have cancer. Of course not. A breast tumor biopsy is performed as standard for any uncertain lesions detected. Research reports that over 80% of the results indicate mild changes.
Questions also often arise as to whether a vacuum assisted biopsy is a good choice. In answer to this question, it is worth mentioning a few points. First of all, it is an innovative test, definitely less invasive than in the case of a surgical procedure. It does not require a hospital stay, therefore it is definitely less stressful for the patient herself and the obtained histopathological material is 100% certain. You should also pay attention to the high accuracy of this type of biopsy. The use of innovative solutions allows for the indication of an almost error-free location of the tumor with an accuracy of 1 mm, and the rotary vacuum system allows the collection of a sufficient amount of tissue for examination in a form that gives reliable results.
For patients, the diameter of the needle with which the procedure is performed is also important. In the case of a vacuum assisted biopsy, it is 2-3 mm, and for comparison, in the case of a surgical biopsy, the incision is approx. 5 cm. So there is only a small trace left after the examination. In addition, it is worth noting that the procedure is performed under local anesthesia and does not require a stay in the hospital, so you can go home after the examination.
VAB is very often chosen by young women because of the small scar left after it has been performed. When it comes to fine-needle biopsy, it should be remembered that it may not be sufficient to make a complete diagnosis, as the histopathologist cannot assess the nature of the neoplasm.
Vacuum assisted biopsy can also be performed after the excision of a benign breast lump, when examining changes in the second breast after amputation of the one with cancer, or in conservative treatment. As with any surgery, also in this case there are contraindications to its performance, and they include: blood clotting disorders, skin infections at the site of the planned VAB, and insufficient immune system.
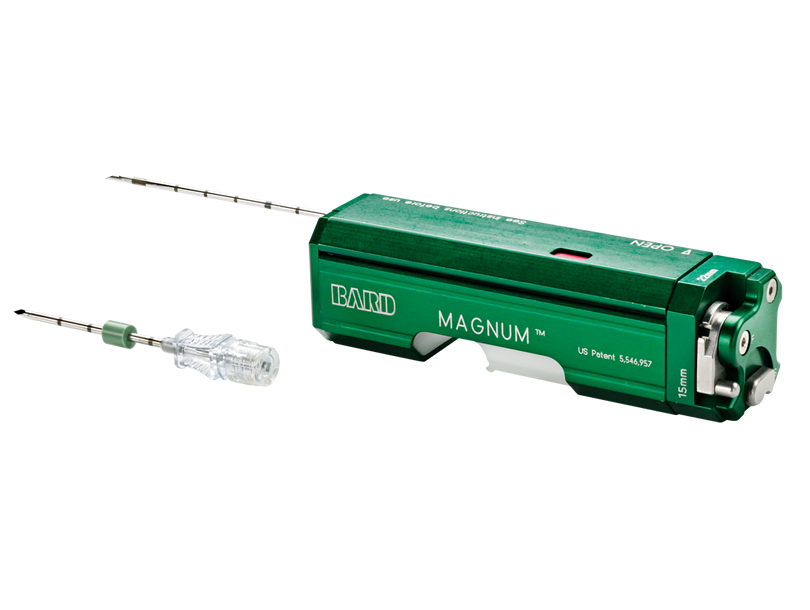
Core needle biopsy (CNB)
It is only a diagnostic biopsy, it is impossible to remove the tumor with this method. The test consists in taking a tissue material, not only a cellular (cytological) material, as in the case of fine needle biopsy (FAC), which is more accurate.
A core-needle biopsy is performed using a special device and a needle with a relatively large diameter (about 3 mm), which penetrates the tumor tissue. A biopsy is performed under local anesthesia, the needle is inserted into the tumor. After the needle reaches the tumor, a trigger mechanism is activated, which causes the needle to be inserted to a depth of about 2-3 cm and a tissue sample is collected. The procedure is repeated several times to obtain the appropriate number of samples for histopathological examination.

Open biopsy (surgical procedure)
It is a classic surgical procedure. Under local or, less often, general anesthesia, the surgeon makes a few centimeters incision in the skin near the tumor. The completely resected tumor, sometimes with a large margin of healthy breast tissue, is sent for histopathological examination. The procedure is performed in the operating room, sutures are placed on the skin, a scar is formed on the outside and inside of the breast. Only with the
Fine needle biopsy (FNB)
One of the methods of collecting cellular material for testing is to use a syringe with a thin needle. An undoubted advantage of the test is that the result is ready for collection after a few days. It should be remembered that FNB is only a cytological test and allows only diagnostics related to the collected cells. This type of examination does not allow for the assessment of the structure of the breast tumor, which makes it impossible to make an accurate diagnosis. It should also be noted that the material is collected with a very thin needle, which in some cases may turn out to be insufficient for diagnosis. If the collected cells are unrepresentative and the structure of the breast lump indicates the likelihood of cancer, the test is repeated by another method. This often results in an unnecessary extension of such valuable diagnostic time.
Fine needle biopsy of the breast should be used mainly for the diagnosis of enlarged lymph nodes. This test is also used in the diagnosis of the thyroid gland, salivary glands and nodules in soft tissues.