This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Prophylaxis
Early diagnosis of breast cancer enables its complete cure
Diagnostic tests of breast cancer performed in its early development give a chance of a 100% cure. This is the case when a lesion is detected that is in a pre-invasive state, i.e. one that develops without lymph node metastasis. However, it should be remembered that with each successive stage of the disease, the chances decrease by 25%. Examination for breast cancer detecting early change has the additional advantage of the possibility of conserving treatment, it significantly increases the quality of life both during the therapy and during the return to normal life.
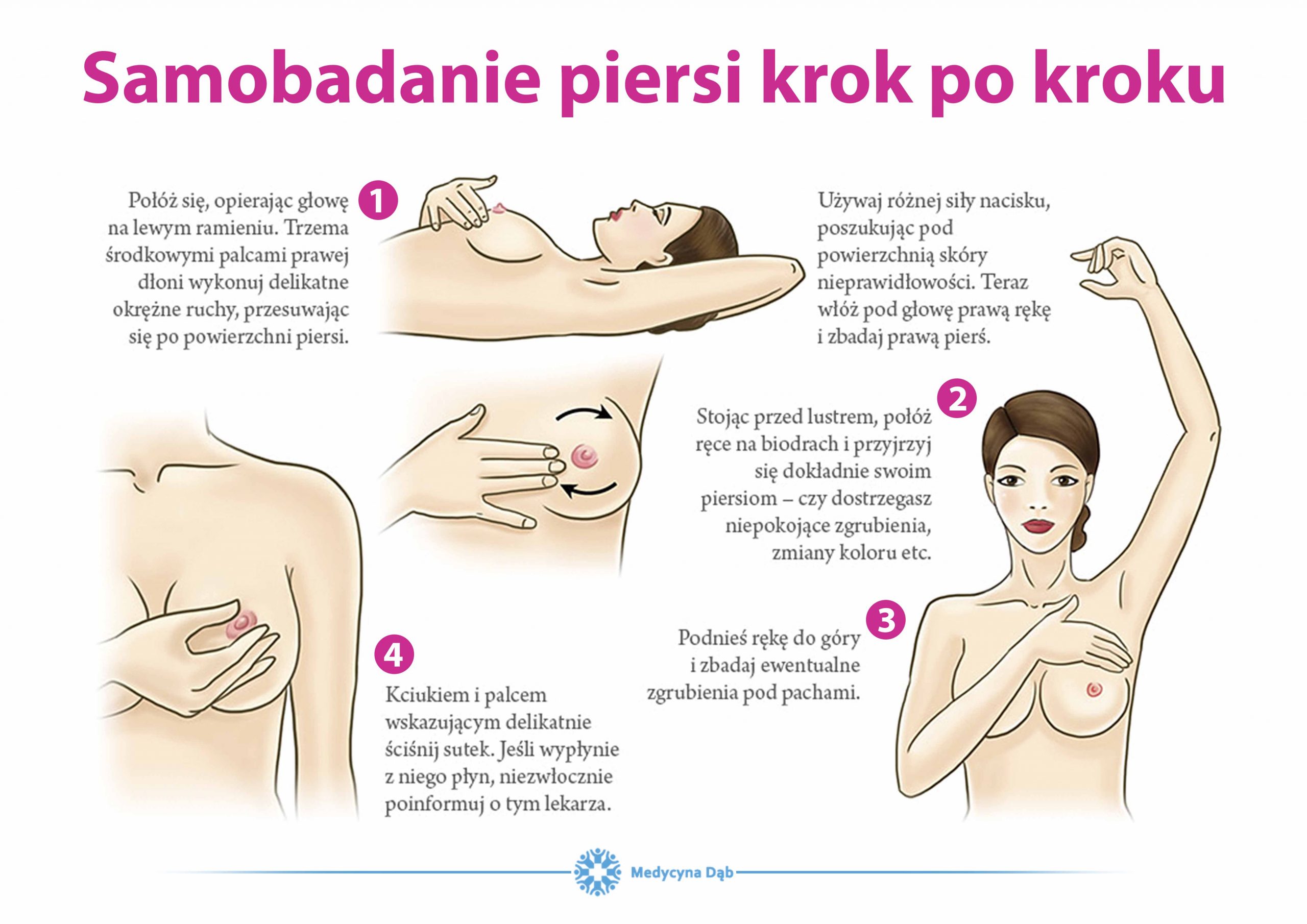
Self-examination is the most popular way to detect many changes in the mammary gland. The gynecologist should also palpate the breasts at each control visit. Research reports that as much as 30% of all lesions are detected in this way. However, it should be remembered that we can palpate a nodule about 1-2 cm in size, while pre-invasive changes are very often only a few milimeters and are usually not detected in this type of examination. This is why it is so important to perform ultrasound and mammography imaging tests, which can detect even the smallest changes.


The causes of breast cancer and an increased risk of developing breast cancer
There are many causes of breast cancer, ranging from idiopathic to genetic. The obstetric history is also important in the diagnosis and examination of the risk of cancer. Women who gave birth to their first child after the age of 35 or had lactation problems belong to the group with an increased risk of developing the disease. This is because the mammary glands do not fully mature until after giving birth. The very conception of a child, in turn, significantly reduces the number of menstruations, and thus the level of estrogen, which in turn prevents the formation of cancer. For the same reason, the high-risk group includes women who have had long periods. If the first bleeding was before the age of 12 and the last one was over the age of 55, this indicates elevated estrogen levels. It should also be remembered that when assessing the risk of disease, all pregnancies, including those that ended in miscarriage, are important. An in-depth medical interview allows for the determination of the risk of developing breast cancer, and thus the introduction of appropriate prophylaxis in the form of much more frequent examinations and visits to the gynecologist. The aim of all these measures is to detect possible changes early, so
that sparing therapy can be used instead of aggressive one.
Genetic research and breast cancer
Currently, it is estimated that genetic burden causes about 10% of all cases. If the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes are mutated, the risk of breast cancer increases by 50% to 80%. The likelihood of developing the disease is also high when the closest person (grandmother, mother, sister) suffers from cancer
Diet and lifestyle during treatment
Diet and lifestyle are important in the treatment process. Limiting the consumption of processed products and products containing preservatives greatly improves not only the well-being, but also supports the therapy itself. The same is true for physical activity. If a woman has already undergone surgery, remember to consult a specialist on what type of sport or exercise would be recommended.
If you are over 20 you should check your breasts regularly.
Remember that:
- you are not testing yourself to find a tumor, but to make sure it is not there
- it is best to check yourself a week after menstruation, and once a month after menopause, e.g. on the first Saturday of the month
- when you notice something disturbing, go to the doctor, do not hesitate
- Don’t jump to conclusions – not all lumps are cancerous, but all lumps should be checked by your doctor.
Why worry. Let your doctor worry. They will certainly not be offended if you visit, and it turns out that you are healthy or that you suffer from a minor disease in the form of cystic degeneration or mastopathy - breasts must be watched and controlled
- despite all the diligence and regularity, do not feel exempt from periodic checks of your breasts at the doctor – a
visit to a breast specialist, gynecologist, family doctor, etc. is a good opportunity